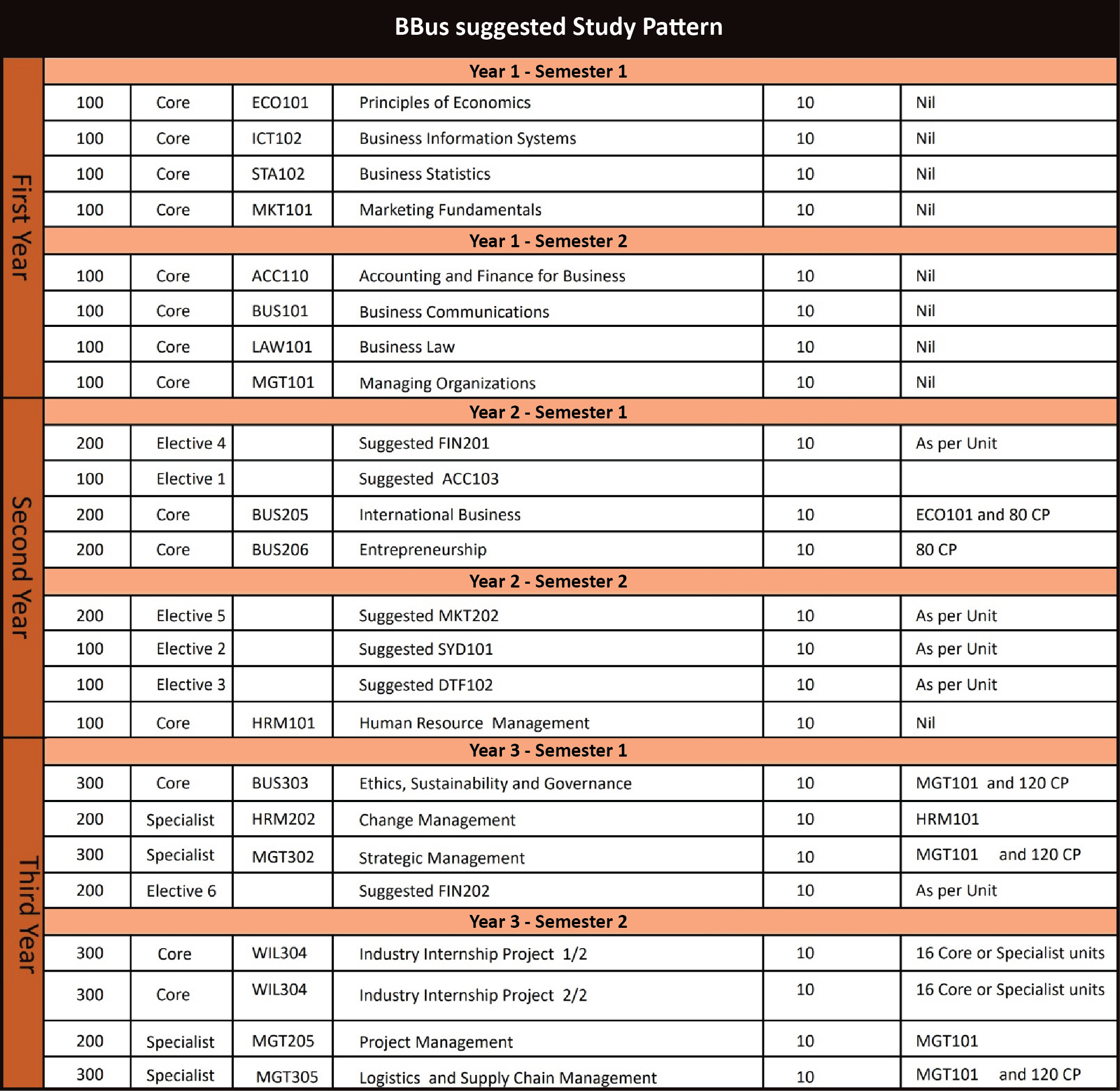
Course OverviewThe Bachelor of Business (BBus) course will provide a broad range of business and management skills, that will be useful to students interested in working in a range of different roles in business. The course is built on a foundation of versatile business-related disciplines, such as, accounting, finance, management, marketing, human resource management, statistics, law, economics, ethics,entrepreneurship, international business, and information technology. Such foundation is then complemented with 4 special units and an Industry-based internship program. In addition, sufficient choice and flexibility is provided in a particular area. |
Duration156 Weeks / 3 years ( Full Time ) |
Study MoodFace to face |
Course Fee$50,400 Total Course Fee | $16,800/Year | $8,400/Semester | $2,100/Unit |
Entry RequirementAs a minimum, applicants must have successfully completed Australian Year 12 or equivalent. ( For country specific requirements, to the entry requirement page) |
English ProficiencyIELTS: Overall score 6.0 (or better) (with no band score less than 5.5) TOEFL: Overall score 60-78 with minimum scores; Reading 12, Listening 11, Speaking 17 and Writing 20 Pearson (PTE Academic): Overall score 50 (or better) (with no score less than 42) Cambridge English: Advanced (CAE) or Proficiency (CPE) with a score of 169 above. No less than 162 in each skill |
IntakesMarch, July, November |
Delivery LocationLevel 4, 303 Collins St, Melbourne, VIC 3000 |
| CLO1 | Demonstrate broad and coherent knowledge and skils inthe field of business for professional responsibility and further learning. |
| CLO2 | Demonstrate well-developed cognitive and technical sks to adapt knowledge and skills to generate practical, timely, and appropriate solutions for complex business problems in diverse contexts |
| CLO3 | Analise and evaluate relevant information to take various short- and ong-term actions in the administration, strategy, marketing, and financial management of a business management of a business. |
| CLO4 | Demonstrate well-developed cognitive and technical sks to adapt knowledge and skills to generate practical, timely, and appropriate solutions for complex business problems in diverse contexts |
| CLO5 | Select and apply appropriate methods and technology to communicate electively with all stakeholders with clarity and comprehension. |
| CLO6 | Apply knowledge and skills with initiative and proper judgment for problem |
| CLO7 | Demonstrate the application of knowledge and skills with independence, responsibility, and accountability for self-learning and professional practice, and collaborate with others within broad parameters.solving and decision-making in professional practice and scholarship. |
ACC110 is a comprehensive accounting and finance unit that provides fundamental knowledge of financial accounting, managerial accounting, and finance. It will help students develop an understanding of the basic accounting equation, the nature and significance of financial statements, common managerial accounting tools, and the finance concepts and techniques applied to organisational decision-making. The unit examines the impact of accounting and finance in business and vice versa, covering topics related to preparing and analysing financial statements, preparing budgets, conducting break-even analysis, assessing risk and return of various sources of funds, and investment opportunities. After completing this unit, students will have a strong foundation in accounting and finance as applied in business decision-making.
MGT101 introduces management and leadership theories and practices. It highlights why effective management and leadership are vital in a globalised and competitive environment. Students will examine the four basic management functions: planning, organising, leading, and controlling. The unit will also help students understand the importance of professional ethics in business contexts. They will learn to identify the essential personal and team skills required for managers to contribute effectively to organisational success in a challenging business environment. Critical areas covered in the unit include developing self-discipline, project planning, effective communication, controlling business operations, managing groups and teams, managing conflict, and managing organisational change.
ECO101 introduces students to the discipline of economics and prepares them for more advanced studies in the areas of business, finance, and accounting. The unit examines how the economy operates at the macro (economy-wide) and micro (unit) levels. Students examine the factors that influence the behaviour of consumers, firms, and markets and the impact of government, taxation, interest rates, and central bank policies on the economy. Emphasis will be placed on applying economic concepts to practical real-life scenarios.
Marketing is central to all businesses as it impacts on the core revenue earning external function, aiming to fulfil the needs and wants of customers while achieving organisational goals This unit provides students with foundational knowledge of marketing as a discipline with a practical focus. Students will learn how key marketing theories, concepts and standards can help businesses make effective decisions. It is specifically designed to employ a variety of examples from both local and global markets, allowing students to research and analyse specific marketing essentials such as consumer behaviours, social responsibility and buying concepts across a range of marketing environments.
This unit introduces students to the Australian legal environment and examines a number of commercial laws that are central to business, such as contract law, law of agency, consumer protection law, insolvency law and law of torts.
It covers contract law provisions, including offer and acceptance, consideration, consent, duress and undue influence, legal capacity of parties, false and misleading statements, breach of contract and remedies. Under tort law, the unit examines provisions relating to negligence.
It also covers various aspects of consumer protection law, such as misleading, deceptive and unconscionable conduct, consumer product warranty and remedies, as well as agency law. Emphasis will be placed on the understanding of ethics and legal reasoning and on the application of legal principles to actual business situations.
This unit is designed to give students the skills to communicate clearly and coherently to engage and interact with a range of stakeholders in a business environment using appropriate language and communication strategies. Through class presentations, role-play and interactions in the class, students will develop skills and knowledge for effective oral and written presentation, including by using technology, and articulate the most appropriate communication style that pays due attention to contextual, social, health and safety, ethical and cultural considerations.
The Business Statistics unit is designed to equip students with knowledge of valuable statistical techniques and procedures so that they can systematically process information to offer meaningful conclusions. Business decision making requires sound statistical data analysis, which in turn requires knowledge of appropriate tools of analysis. Topics covered in the unit include knowledge of data and data visualisation techniques, probability distributions, sampling and statistical inferences, hypothesis testing and regression techniques. The unit incorporates current cases and hands-on exercises to reinforce the basic statistical principles. Analytical tools incorporated in the unit include the use of spreadsheets, tables and statistical/financial formulas and calculators to solve problems. The statistical skills students acquire from studying this unit represent essential tools for success not just in today’s complex business world but also in their own personal finance planning.
HRM101 provides a comprehensive overview of HRM policies and strategies and gives in-depth coverage to the major functional areas involving managing people in an organisation. It focuses on specific areas of HRM policies and practices, such as staff planning, hiring, training, compensating, motivating, leading, team building, and maintaining a culture of equity and fairness in the organisational HRM.
The unit explores the critical importance of managing human resources effectively within organisations and their increasing complexity nationally and internationally. Students will be provided with an understanding of ethical and socially responsible perspectives of HRM. Relevant HRM theories and models that explain the nature and importance of various HRM practices and their outcomes will be considered and assessed.
Students will learn about the skills to deal with employees and fellow staff in maintaining a healthy work culture. The unit will also inform students of their rights and obligations as employees.
Business success requires an understanding of how technology can be used to not only assist with the operational aspect of an organisation but also to streamline the decision-making process in areas ranging from marketing through to manufacturing. In this unit, students will learn how to use the various computer software and Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) to assist in decision making and in the supply-chain management process. The unit involves IT fundamentals, practical use of Excel spreadsheets and graphs, value chain analysis, E-business, managing information system (IS) infrastructure, outsourcing data, information and database management, social media, customer relationship management, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and use of Power Point for presenting case solutions. Students will explore several ICT and social media tools to enhance their digital literacy and solve various business problems by using modern IS tools.
BUS206 introduces entrepreneurship, from theoretical understanding to application of the principles of business creation. The unit will enable students to understand the fundamental concepts and processes of entrepreneurship to gain an insight into the entrepreneurial venture. Topics include definitions of entrepreneurship, types of entrepreneurs, nature and importance of entrepreneurs, the advantages and disadvantages of being an entrepreneur, the venture creation process, developing a business plan, legal issues for entrepreneurs, sources of information and funding advice, business tools, and other aids for entrepreneurs.
Maintenance of sound ethical standards and a sound corporate governance structure are absolute essentials for ensuring a responsible and sustainable business. Great social and economic responsibility is imposed on anyone involved in business generally (including directors, managers and other responsible persons) and on accountants specifically. Those in positions of responsibility are relied on and trusted by society for upholding high ethical and governance standards and to ensure that such a culture exists across the entire organisation. This unit introduces learners to the essential concepts of business ethics and corporate governance and exposes students to principles and concepts for personal and organisational ethical decision-making.
Ethics and governance are intertwined concepts in professional life for business leaders. Accordingly, this unit offers a rich and dynamic examination of ethics and governance from the viewpoints of different stakeholders such as businesses, employees, the government, their suppliers and their customers. Key areas covered include: business, society and corporate citizenship; fundamental issues and theories of personal, business and corporate ethics and governance; ethics and global business, the APESB and APES 110, public policy and technology; internal and external stakeholders; and consumer rights and environmental expectations. Case studies and extensive class discussion using audio-video clips will be used to enrich the learning process.
The growth of international business is greatly influenced by changes in the international business environment, war, natural disasters and other unpredictable events. These types of issues and events raise strategic challenges for any business. This unit introduces students to the global legal, economic and political environment of international business. It examines global business strategies focusing on ethical practices, entry strategies and global management of international business. Specific focus is given to global human resource management and understanding how to manage an international workforce.
Growing international business requires an understanding of global marketing. Students will be introduced to methods of analysing international markets and marketing intelligence systems. Students will apply their knowledge to devise international products and promotion of international products demonstrating key learnings relevant to international pricing and customers. Extending international business also necessitates knowledge of global operations and supply-chain management. Finally, students will also focus on global fiscal management and have foreign exchange knowledge.
MGT302 introduces students to the major concepts and tools required for strategy formulation and competitive analysis in a business environment. It examines the processes and techniques employed by managers to ensure the survival and high performance of their enterprises. These measures involve devising strategies, identifying market and firm boundaries, and maximising the internal and external strengths of the firm.
Business strategy requires managers to consider customers, suppliers, competitors, economic and technological trends, financial markets and government regulation, and the forces brought about by globalisation. Key issues examined include identifying and choosing competitive strategies; critically examining competitive advantages, threats and opportunities for the firm; and achieving and maintaining competitive advantage and market leadership. The relevant topics include product differentiation strategy, cost leadership strategy, price-skimming strategy, innovation strategy, growth strategy, acquisition strategy, focus strategy, and exit strategy.
Case studies and case analysis will help students apply concepts and frameworks to real-world examples and think strategically when implementing business processes and structures.
MGT205 builds on the art and science of management by providing the knowledge and tools to successfully manage a wide range of projects of various sizes and complexities across multiple sectors. It will help students enhance their capabilities in project planning, supply-chain management, budgeting, scheduling, managing teams, and managing risk. Students will learn the fundamental concepts of project management: Scope Management, Cost Management and Time Management. They will analyse project situations and learn how the principles of project management interrelate in a project environment. Students will gain the skills to successfully manage projects in various sectors, including construction, manufacturing, engineering, trading, information technology, and social and commercial events.
HRM202 provides an understanding of change in organisations — its dynamics and how to manage it. Students will learn techniques for documenting and addressing the complexities and challenges that change imposes on organisations. This unit explores the impacts of the key drivers of change: technology, globalisation, consumer rights, government policy and regulation, organisational power-shift, and natural disasters such as pandemics. Students will develop an appreciation and awareness of innovation, expectations and the emotions associated with implementing change in organisations.
MGT305 will help students design and implement supply chains that are efficient and economical.
Logistics and supply-chain management encompass all activities, processes, and movements in an organisation to ensure a smooth flow of materials, machinery, and human and other resources. It streamlines all supply-side activities to maximise customer value and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. In recent years, disruptions such as COVID-19 have significantly challenged this essential area of managerial responsibility.
The unit covers everything from product development to manufacturing to distribution to the information system needed to achieve a seamless flow of goods and services. Students will learn how to control information systems centrally and link all production, distribution, and transport systems to deliver products on time. The areas of focus of the units include formulating an appropriate and sustainable supply-chain strategy, sourcing input resources, inventory control, production management and scheduling, transport management, and information systems design and management. Assessment of the unit will involve some group activity and an oral class presentation.
WIL304, which includes an Industry Internship, requires students to demonstrate their capabilities in dealing with the complex problems of real-life organisations, which is essential to complete a learning cycle. It is a comprehensive unit that offers students an opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills acquired earlier in the course and apply them in cross-disciplinary contexts to identify a business issue, articulate thoughts, investigate the key issues, and advance feasible solutions. The material outcome of this empirical exercise, which integrates theoretical concepts and applies organisational solutions to an identified problem, culminates in submitting a report followed by delivering an audio-visual presentation in front of an internal and external audience.
Students will work in small groups at a host organisation’s venue to conduct a field study on a particular business problem or a host of problems. By revisiting the scenarios, theories, case studies and exercises completed in the taught units in the course and using self-reflection and mentoring feedback, this unit will sharpen the students’ skills and make them confident in applying their knowledge to diverse business problems. Thus, this unit will prepare students for line responsibility in a business or help them execute client-based consulting projects.
The proper costing of products and services is critical for the survival and success of a business. Cost and Management Accounting provides organisations with internal financial and non-financial information required for the important functions of planning, controlling and decision making. This unit enables students to develop an understanding of the elements of cost and management accounting and the way in which cost information is used in undertaking critical functions within a modern business organization. It covers cost behaviour analysis, activity-based costing, standard costing, budgeting and cost control and a range of basic management accounting theories for strategic decision making. The unit will help students to develop their analytical skills and awareness of ethical and socially responsible decision making.
DTF102 examines how organisations use databases in various contexts, from local databases to enterprise databases. Students will develop the knowledge and skills to design a relational database. The unit covers different database technologies and forms of database management, various data–modelling approaches and concepts, and different database–development processes.
SYD101 shows students how to analyse business problems and opportunities from the perspective of systems analysis using graphical modelling techniques to represent the design of current and proposed new information systems. Such analysis is necessary because computer-based information systems implement business requirements as technology solutions. Students will use modelling methods such as Structured Design and Object-Oriented Design to develop new designs. By using one of several forms of a Systems Development Life Cycle or purchased software package selection, they will learn about design implementation.
MKT202 studies the rational, emotional, and behavioural processes consumers rely on to use (or consume) products and services. It incorporates ideas from several sciences, including psychology, sociology, biology, chemistry, and economics, to explain consumer response to a new or existing product or service. The unit aims to help students analyse the impacts on consumer buying behaviour of psychological factors such as personality, perception, motivation, needs and attitudes, and environmental factors such as culture, socio-economic class, family and friends, and overall educational levels. This study will help students determine gaps in the market and identify the products and services that are needed or are obsolete or out of fashion. It will also help them understand what influences consumers to choose between various options, how they feel about different brands, and how to present the products to generate maximum impact on consumers’ buying behaviour. The insight acquired from this unit will enable students to formulate an effective marketing strategy.
The ACC204 Financial Accounting and Reporting unit builds on the ACC101 (Principles of Accounting) and ACC102 (Accounting Information Systems) units to give students an in-depth look at how more complex and industry specific issues are reported in Australia. It also delves into the principles and ideas applied in measuring and reporting on a range of items in the balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement.
Topics covered in this unit include: revenue recognition, accounting and reporting for tangible and intangible assets, liabilities, income-tax, leases, foreign currency transactions and accounting for financial instruments. Preparation of cash flow statements is also covered. This unit is aimed at broadening the horizon of accounting knowledge of the students in specific types of issues that they might encounter in real life.
Accounting for companies requires special knowledge and skills, as they have specific legal reporting formalities to comply with. Moreover, prevailing accounting standards are more obligatory for companies than other types of business entities. This advanced financial accounting unit enhances students’ knowledge and skill to handle accounting requirements for corporations.
This unit covers Australian accounting standards vis-à-vis international financial reporting standards, Australian reporting requirements for listed and unlisted public and private companies and other incorporated bodies. Topics covered include accounting for shares and bonds, accounting for equity investments and joint ventures, accounting for group structures involving parent and subsidiary companies, accounting for intra-group transactions and minority shareholders, fair value accounting and impairment of assets. Overall this unit provides student with a solid conceptual understanding, practical techniques and methods for approaching some of the most challenging accounting problems of the corporate world.
This unit introduces students to corporate regulation in Australia and a range of legal issues faced by various forms of commercial and incorporated entities in Australia. Important issues that will be examined include various forms of incorporated entities, formation, registration and legal status of different types of companies; company constitution, legal rights, duties and obligations of creditors, shareholders and directors; company prospectus and capital raising; issue of various classes of shares and share buy-backs; corporate governance, meetings, types of resolutions, and voting, disclose documents and ASIC lodgement, company restructuring and liquidationl; voluntary administration and receivership; rights of creditors and division of assets in case of a liquidation. This will provide students with a thorough understanding of principles guiding the operations of corporations.
This unit aims to provide students with practical working knowledge of all aspects of Australian taxation law. It is designed to enable students to understand and apply the basic taxation legislation and analyse relevant taxation cases and rulings. The unit is aimed at providing students with an understanding of Australian personal and corporate income tax, fringe benefit tax, capital gains tax, and goods and services tax. Key areas covered include assessable income and allowable deductions for individuals, and a variety of business entities including companies. Emphasis is placed on the application of legal principles to actual business situations including the general anti-avoidance provisions. Emphasis will be placed on the application of legal principles to actual business situations.
The Corporate Finance unit examines the basic concepts, principles and theories of business finance. The unit aims to provide the students with the opportunities to learn the techniques of compounding and discounting underlying the concept of time value of money and understand the nature of trade-off between risk and return of an investment. The unit will also help students gain a thorough understanding of the role of debt and equity as components of an entity’s capital structure. It will also examine the critical role of cost of capital and cash flows in the evaluation of shares, bonds and investment projects.
A combination of the above knowledge and analytical skills, coupled with an understanding of the relevant capital market theories, will enable students to make informed decisions about financing the business, selecting the right investment project and valuing existing and potential investment options. These concepts and principles will be discussed in the context of local and international capital markets.
In order for a business to successfully operate in an increasingly complex financial world, a good understanding of the nature, complexities, risks, and possible returns from available financial instruments and of the players in the market is essential. This unit aims to increase the students’ intellectual capabilities in understanding the tools and instruments used by the share market, bond market, commercial and merchant banks, insurance companies, credit unions, investment funds and the derivatives market. The topics in the unit will cover the critical features of various types of shares and bonds, unit trusts, and derivative financial instruments such as forward contracts, futures, options and swaps. Accounting as a financial discipline will remain past-focused unless it can capture the activities, risks and returns of the financial markets, and hence this unit navigates students through the complex world of financial markets.
FTP202 introduces students to the basics of programming, covering such concepts and topics as variables, control structures, and arrays. The unit will also include software design and testing, development, and implementation. Java Programming (JP) software will be used for practical work, including development, and the unit will deal with coding standards and testing strategies.
ACC308 is prescribed to open a window on forecasting the future with the help of some structured mathematical/statistical tools. The unit combines knowledge and skills from accounting, economics, finance, mathematics and statistics, and business strategy to conduct a meaningful analysis, business valuation, and forecast for a business.
The objective is to use other appropriate statistical methods and models to synthesise and analyse available data for statistically predicting the important future decision variables, such as demand, competition, price, cash flows, earnings, interest rates, exchange rates, production costs and share prices. One of the most important functions of management is to conduct financial analyses to anticipate and manage uncertainty. Business forecasting is an essential technique for that.
In this unit students are exposed to the underlying concepts, objectives and techniques of the auditing and assurance process. It explores the key issues of auditor independence and ethical dilemmas of an auditor. Students will gain an understanding of the nature and purpose of auditing, the audit process, and the responsibilities of auditors in fulfilling their duties.
Critical areas covered include: ethical responsibility and legal liabilities of auditors and clients, assessment of internal control and audit risk, examination of audit evidence, detection and prevention of fraud, and various forms of audit reports. The unit covers the contents designed to meet the preliminary requirements of CPA Australia (CPAA) and Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand (CAANZ).
This unit covers statistical data analysis methods, financial mathematics, probability analysis, and forecasting. The analytical tools include spreadsheets; financial tables and statistical or financial formulas and calculators; regression and probability analysis; and time series analysis.
Because of the interdisciplinary and analytical nature of the unit, it will be a suitable preparatory course for the Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Chartered Accountant (CA), and Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) programs. It will also be helpful for those who are planning a career in investment banking, investment analysis, fund management, business consulting, corporate finance, or public accounting.
Accounting theory represents the ‘science’ of accounting. This third year unit requires students to understand the science and theoretical background underlying accounting. It helps them to critically explore the logical reasoning behind various accounting tools and practices. It also critically explores the accounting regulatory framework. The epistemology of accounting theory and theory development is discussed. Distinction is drawn between hypothesis and theory, and between positive and normative accounting theories. The unit examines the political process of accounting standard setting and the economic and social consequences of accounting standards. The unit also discusses some contemporary accounting issues that are currently being examined, such as, environmental accounting, human resource accounting, harmonisation vs. standardisation of accounting, and the role of accounting in corporate governance and audit failures.
The course aims to offer a comprehensive program that contains an appropriate balance
of general and specialised knowledge and skills to produce well-rounded graduates; and secondly , to foster a range of transferable skills that will enhance graduate employability. Lyons College Bachelor of Business graduates are expected to find employment across the corporate sector, industry, g overnment an d in n on-profit organisatons, among others. According to the occupations list published by the Australia and New Zealand Standard Classification of Occupations (ANZSCO,2021) the Bachelor of Business graduates will qualify for employment in one or more of the following occupations:
Sign up to our newsletter and receive information about new courses, promotions, offers and succes of Lyonians.





